In mathematical logic, a predicate is commonly understood to be a Boolean-valued function. However, we use the extended notion of a logical type instead of Boolean. And a predicate can return three values: true, false, and none (undefined).
If the predicate returns none, you must treat this as an exception. For example, a timeout occurred. none means that the predicate could not calculate true or false.
To create a predicate within the semantic model, you must type the keyword def. Then the predicate pattern appears. And you can specify the name of the predicate, its arguments, and the body of the predicate, which is a logical expression.
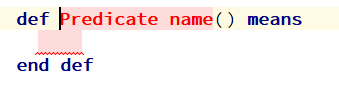
The predicate name may contain spaces. Also you can use not only Latin, but also other national alphabets ..
The predicate pattern is created without arguments. To add an argument, place the cursor inside the parentheses and press Enter or Insert.
The predicate body can be any logical expression of d0sl language: and, or, not, check all, if, for all.
But for simplicity, we advise the body of the predicate to start with the check all instruction. check all instruction is equivalent of and instruction with many arguments each is in new line.
Predicate example
def check board(board : ChessBoard) means
check all
var queens = ChessDSL.get queens(board)
for all q1, q2 in queens
not ChessDSL.on one line(q1, q2) and
not ChessDSL.on one diagonal(q1, q2)
end
end def